
TLDR: In this issue
The Quantumrun team shares actionable trend insights about creative ways to generate solar energy, the potential collapse of the Gulf Stream, the increasing pivot to autonomous warfare, and questioning the hype behind the LK-99 superconductor.
Future signals to watch
25 countries have reduced multidimensional poverty by half within 15 years, with India leading this progress.
Universal Music Group and Google are discussing the possibility of licensing artist melodies and vocal tracks for use in songs created by artificial intelligence (AI).
The average American workday got half an hour shorter, with productivity unchanged 👏👏👏
Autonomous vehicles are projected to contribute as much as 20 percent to global gross domestic product within 10 years.
Researchers from China have created a flexible, powerful design for a customizable whole tumor cell vaccine.
The US Navy’s robot ships and submersible drones represent another signal leaning us into the era of autonomous warfare.
The LK-99 superconductor, touted as “the physics breakthrough of a lifetime,” might help industry reduce the size of all electronics, accelerate the uptake of national renewable energy grids, and could even accelerate the development of nuclear fusion. Sadly, the Quantumrun team is still skeptical of these early results; other science labs are having trouble recreating the experiment. Hoping for the best, but we’ll know by September if this is the real deal.
Finally, videos can be automatically reformatted to fit any size/resolution thanks to generative AI. Love how our fav movies can now be re-engineered for our phones, vertically.
Solar energy production is getting creative
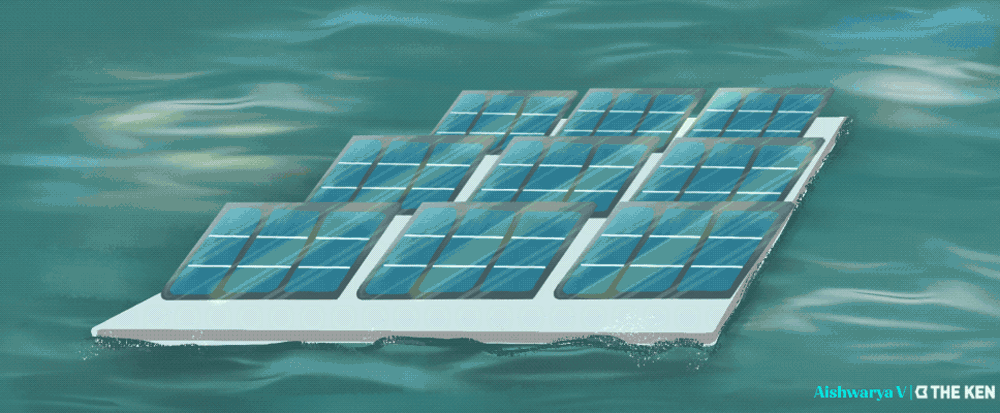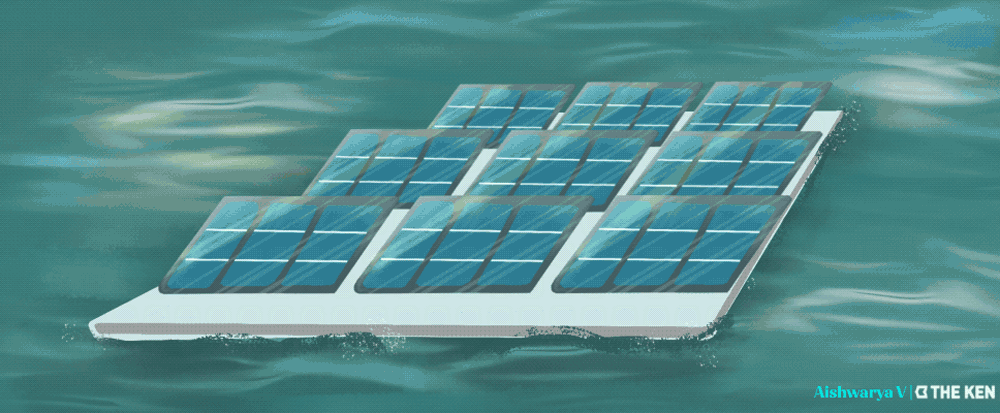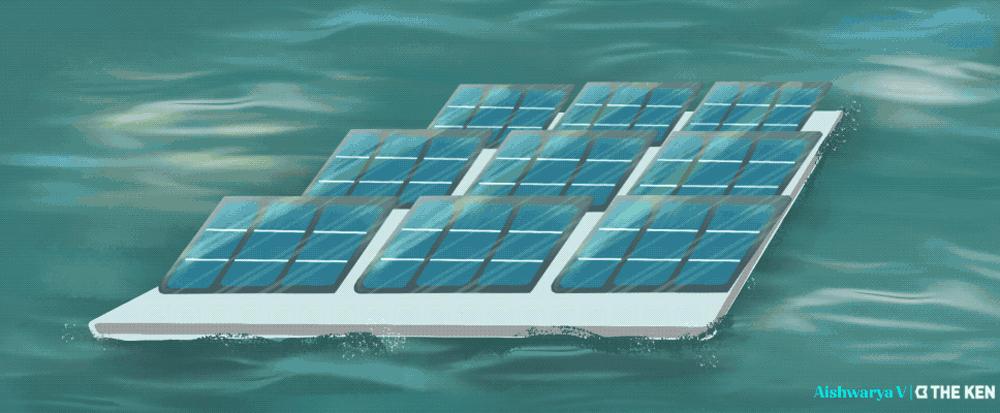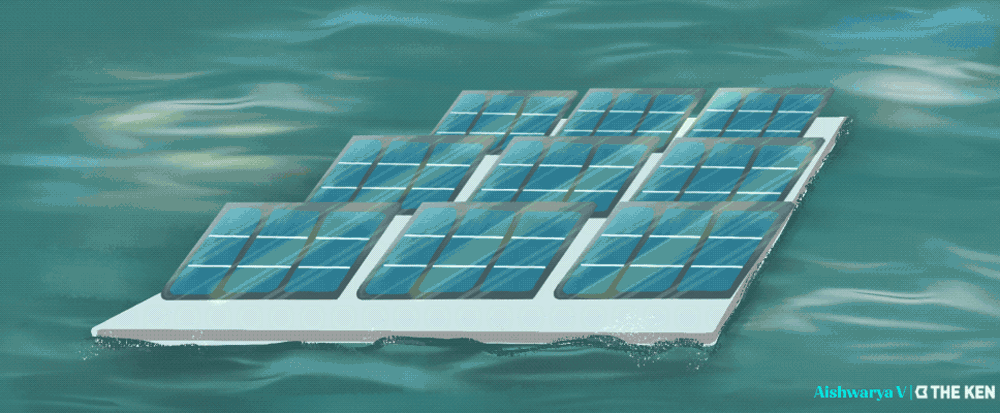
Agrivoltaics and floating solar panels are emerging techniques that capitalize on solar energy. Agrivoltaics, the practice of growing crops under solar panels, has been found to create a cooler microclimate for farm soils, increasing the efficiency of the panels and reducing water usage for crops. This method has helped farmers in hot and dry regions like the American West, increasing crop yield and water efficiency. For example, agrivoltaic cherry tomatoes were 65 percent more water-efficient.
In Canada, agrivoltaics is being explored to meet food and energy needs. Studies have shown that crops like corn, lettuce, potatoes, and tomatoes increase yield when partially shaded with solar panels. This method conserves water and protects plants from excess sun, wind, hail, and soil erosion. Agrivoltaics is also being used to shade and graze sheep. However, barriers like regulations and capital costs are hindering widespread adoption (2023).

Meanwhile, floating solar panels near the equator offer a unique solution to harness solar energy without occupying valuable land. This approach is particularly beneficial in regions near the equator with abundant sunlight. By placing panels on water bodies, countries like Singapore are generating energy more efficiently due to the cooling effect of water and reduced water evaporation.
Ocean regions near the equator also experience fewer storms, so protecting offshore floating solar panels is possible with relatively inexpensive engineering structures. The heat map below shows the Indonesian archipelago and equatorial West Africa as having the greatest potential for offshore solar. (Grey lines show tropical storm paths.)
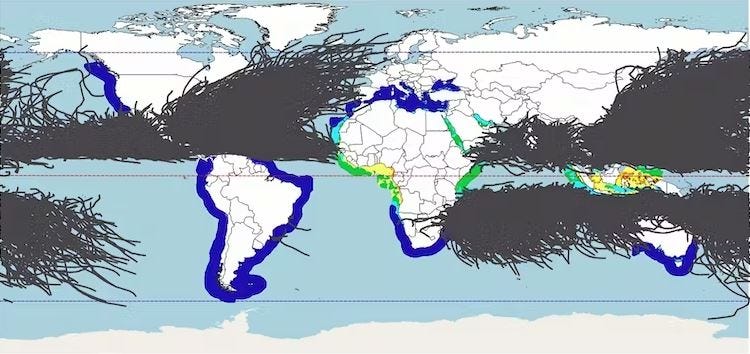
Actionable trend insights for the growing agrivoltaics and floating solar market
For entrepreneurs: They can establish agriculture-specific solar installation and consultancy services focused on helping farmers and landowners implement agrivoltaic systems. Such businesses could offer tailored solutions, from design to permit filing to installation, as well as financing—all to maximize agricultural and energy outcomes.
For corporate innovators: Large corporations with expansive campuses, such as tech firms, can integrate agrivoltaic systems into their landscapes. Growing crops under solar panels can generate renewable energy and support local food banks. Companies in the energy sector can collaborate with universities and research institutions to drive innovation into floating solar research and development. This technology could help reduce evaporation levels of fresh water in domestic lakes and outdoor reservoirs, particularly as global warming continues to increase temperatures.
For public sector innovators: Government agencies can develop education programs to promote agrivoltaic practices among farmers and communities. By providing training, resources, and tax incentives, they can encourage the adoption of this sustainable approach. For example, a local government might launch a pilot program to transform public parks into agrivoltaic spaces, serving as a model for urban sustainability. Public sector entities can also identify suitable water bodies and collaborate with private partners to create significant renewable energy sources.
Trending research reports from the world wide web
This report shows where COVID’s new variant, EG.5, is spreading in the US.
A deep dive into the NVIDIA GPU bottleneck that may slow down AI innovation.
Big Tech’s expansion into financial services is in full swing. Apple said that its Savings Account service, run by Goldman Sachs, has collected over USD $10 billion from users since it started in April.
75% of Internet bandwidth across the Pacific, the Atlantic, and Intra-Asia is used by content providers … the Internet has transformed into an entertainment machine under our noses.
Climate change is wreaking havoc on the Gulf Stream system

A recent study warns that the Gulf Stream system (also known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation or AMOC) might fail between 2025 and 2095 if we don't cut carbon emissions. This vital ocean current moves warm water north and cool water south, helping to balance the world's climate. But, melting ice from Greenland due to global warming is adding too much fresh water, which could cause the system to collapse.
If this happens, it could lead to serious global problems. Rain needed for food in India, South America, and West Africa could be disrupted. Europe might face more storms and colder temperatures, and sea levels could rise on the east coast of North America. It could also put the Amazon rainforest and Antarctic ice sheets at risk.
In addition, the ocean’s food web is severely threatened by rising temperatures. Phytoplankton in a warmer ocean lack the essential nutrients they require. Consequently, they generate fewer pigments, which are vital for converting sunlight into energy.
Scientists agree that these trends are a serious concern and need urgent action. The study, led by climate physicist Peter Ditlevsen, used data on sea temperatures from 1870 to predict when this might happen. These results contradict the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)'s assessment that the system wouldn't fail this century, which Ditlevsen believes might be too cautious. While the potential consequences of the AMOC collapse might not be as dramatic as shown in the 2004 film "The Day After Tomorrow," scientists agree we need to act now to avoid a potential climate disaster.
Actionable trend insights as global warming affects ocean systems
For entrepreneurs: They can create startups focused on climate technology, including developing innovative solutions to mitigate climate change effects, such as carbon capture technologies, climate-resilient agriculture, and advanced weather forecasting tools.
For corporate innovators: Firms can integrate sustainability into their business models, including reducing emissions, investing in renewable energy, or implementing circular economy principles. Companies that prioritize sustainability not only contribute to climate change mitigation but can also enhance their reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Multinational corporations can also invest in climate risk assessments, including risks related to supply chain disruptions, assets, or regulations associated with climate change policies.
For public sector innovators: Governments can implement robust climate policies, including regulations to reduce corporate emissions, incentives for renewable energy and green building retrofits, or funding various research into how marine ecosystems are being affected. Governments can also collaborate to fast-track research in climate technology and ocean monitoring through satellites and underwater drones.
Outside curiosities
This is what it looks like when generative AI inspires creativity.
Barbie director Greta Gerwig just became the first solo female director to join the $1-billion-box-office club, which includes James Cameron, Peter Jackson, and Christopher Nolan.
Gen AI is really out there doing everything - from generating images to animating them.
The good news: there’s a rise in remote job listings. The bad news: there’s a decline in the volume of all job listings.
The current national boundaries inside the African continent were drawn arbitrarily by past colonizers. Here's what the continent would look like if its borders were drawn along historical tribal/ethnolinguistic divides.
More from Quantumrun
Read more daily trend reporting on Quantumrun.com
Subscribe to the Quantumrun Trends Platform (free for premium newsletter subscribers)
Corporate readers can review our Trend Intelligence Platform
Follow us on Linkedin
Follow up on Twitter
Email us at contact@quantumrun.com with questions or feedback.
Finally, share your thoughts in the Substack comments below. We love hearing from you!
David Tal, Quantumrun President: Interested in collaborating with the Quantumrun Foresight team? Learn more about us here.
See you in The Futures,
Quantumrun



