The Futures - No. 27
The end of obesity / Artificial wombs / South Korea’s anti-aging breakthrough
In this issue
The Quantumrun team shares actionable trend insights about the possible end of obesity and its societal impact, artificial wombs nearing human trials, continuing US college enrollment woes, and South Korea’s breakthrough anti-aging discovery.
Future signals to watch
South Korean scientists have created a new method to specifically take out old cells while keeping the healthy ones, which could help treat diseases linked to aging.
Students are rethinking the value of higher education. US community colleges are expanding their dual-enrollment program (high schoolers taking college courses) to supplement income amidst declining college enrollments.
Forecasting agencies are now using machine learning to analyze large data sets from various sources like runway shows and social media, helping them identify emerging trends more accurately and swiftly.
Lockheed Martin, Westinghouse Government Services, and Intuitive Machines have been granted contracts by the US Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) to develop nuclear fission solutions for spacecraft.
Large language model apps can simulate the responses of a priest, rabbi, or swami on your screen, signaling a shift to digital spirituality.
The National Association of Realtors (NAR) shared that there's been a notably quick adoption of AI tools by real estate firms, including enhancing presentations and using valuation models to find the best pricing.
The Ocean Cleanup Project extracted over 11,300 kilograms of plastic from the Great Pacific Garbage Patch in one journey.
Fast Company's study reveals that over half of Florida's 410 municipalities will face the impacts of 6.6 feet of sea-level rise, with nearly 30% of the total local revenues from 211 municipalities coming from buildings projected to experience chronic flooding, possibly by century's end.
Are we close to ending obesity?
The emergence of new anti-obesity drugs is carving a pathway to potentially alleviate the global obesity issue, with companies like Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly leading the charge. Initially developed to address diabetes, these drugs have shown significant promise in reducing appetite and promoting weight loss by mimicking a gut hormone. Notable offerings, such as Novo Nordisk's Semaglutide (branded as Wegovy), have reportedly reduced severe cardiovascular events by 20 percent in overweight individuals with a history of heart disease. Eli Lilly's Tirzepatide is under consideration for approval in obesity treatment after being sold for diabetes management under the brand name Mounjaro.
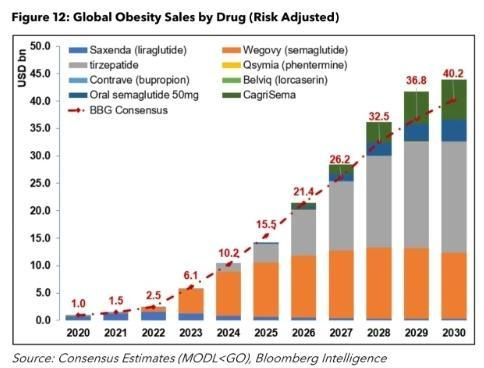
With obesity being a significant health concern linked to numerous chronic conditions and a substantial economic burden to national health networks, these developments hold promise. However, they also spell challenges for the food, fitness, and medical industries, which have long capitalized on the economic opportunities created by obesity management. For instance, reduced demand for non-drug weight management products, services, and specific medical procedures is foreseeable.
Likewise, the food industry, especially companies specializing in calorie-rich products, might witness shifting consumer behaviors—e.g., people who experience weight reduction might be motivated to shift to healthier diets, while others may exploit these drugs to indulge and double down on unhealthy diets.
However, the comprehensive impact of these drugs remains uncertain, given their cost, side effects, and the yet-to-be-determined extent of their adoption. Insurance coverage and the long-term health effects (to be determined by the late 2020s) are among the factors that could influence the uptake of these drugs and their broader societal impact. While the market for these drugs is expected to expand significantly (reflected in the soaring market values of Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly), these treatments introduce a complex narrative of hope, economic shifts, and a re-evaluation of health-centric products and services.
The best-case scenario is an emerging future (late 2030s) that sees countries registering nationwide decreases in preventable diseases and other health concerns, reduced national healthcare costs, and the elderly living healthier, more independent lives.
Actionable trend insights as the adoption of anti-obesity drugs increases
For entrepreneurs: They could consider opening wellness clinics and online platforms that offer personalized advice, support, and monitoring for individuals using or considering these anti-obesity drugs. Moreover, launching analytics ventures that specialize in analyzing health data to provide insights on the effectiveness and impacts of anti-obesity drugs could be invaluable for refining treatment plans and contributing to developing next-generation anti-obesity drugs.
For corporate innovators: Companies in the food and beverage industry might find product diversification essential to align with potential shifts in consumer behavior towards healthier choices. Firms selling weight loss products can also consider reformulating their supplements to complement anti-obesity drugs or partner with other ancillary businesses (such as those treating sleep apnea caused by obesity) to further diversify their market. Moreover, forming strategic partnerships with pharmaceutical entities could lead to collaborative efforts promoting holistic wellness instead of simply treating obesity.
For public sector innovators: Government agencies have the opportunity to establish a supportive policy framework that facilitates the research, safety protocols, and distribution of anti-obesity drugs, ensuring broader public access and benefit. For instance, introducing policies that encourage clinical trials that target various demographics and ethnicities while ensuring safety could accelerate the efficacy of these drugs. Furthermore, boosting public health programs and partnering with educational institutions can help inform people about the different choices they have when pursuing health and wellness, including considering anti-obesity treatments.
Trending research reports from the World Wide Web
Deloitte discusses how companies can take advantage of the growing carbon net-zero marketplace.
A study by Berlin universities demonstrates that producing green hydrogen from sunlight can become profitable by using some hydrogen to transform raw biomass-derived chemicals into industrial chemicals.
Fast Company discusses why we are on the verge of mass commercializing AI companions.
A Google report delves into the information-seeking behaviors that marketers should recognize and respond to, enabling them to swiftly adjust to evolving demand and furnish consumers with the desired products and experiences.
This article discusses how policymaking should develop to adapt to the evolving capabilities of generative AI, particularly in the media industry.
What does the human trial of artificial wombs mean for future babies?

The discussion around artificial wombs is gaining attention, particularly for their potential role in tackling the serious issue of preterm births, highlighted by the World Health Organization as a leading cause of death for children under five years. Guided by the US Food and Drug Administration, experts are gathering to talk about the rules and moral considerations for testing this technology on humans, following promising results in animals. Earlier studies have shown that artificial wombs can help premature lambs grow, which is a big step towards human trials.
The goal isn't to replace natural pregnancy but to assist in the critical growth of babies born before 28 weeks, a stage known as extreme prematurity. Two different designs of artificial wombs are being studied—one is known as the "Biobag" by the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, and the other is called the "artificial placenta" by the University of Michigan.
Biobag method by the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
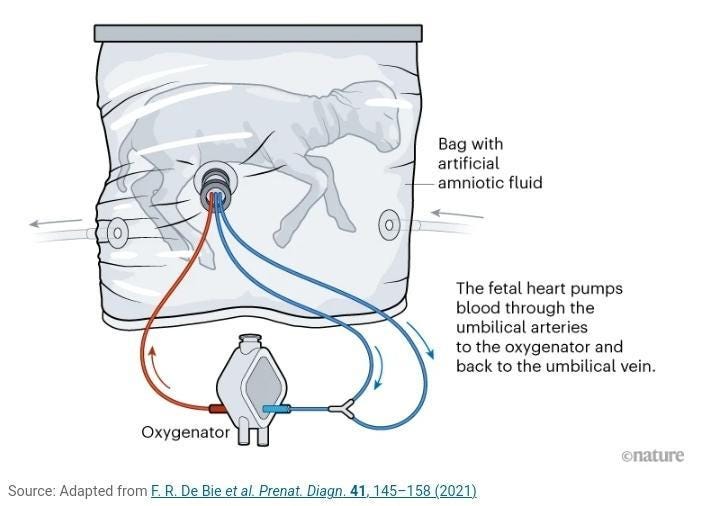
Each has its benefits and hurdles, especially around how the baby is connected to the artificial womb and how long the technology can support life. While there's a growing hope around artificial wombs, they also raise deep moral and societal questions, especially in the US, where reproductive rights are a hot topic. For example, will these methods eventually replace pregnancy and allow corporate or national entities to “mass-produce” humans? How will this redefine what constitutes “life,” particularly in the tension-filled realm of abortion rights? Meanwhile, some experts suggest a wider focus on understanding and preventing premature births, seeing artificial wombs as a small fix to a big issue.
Actionable trend insights as artificial wombs enter human trials
For entrepreneurs: They could delve into creating personalized nutrient formulations for artificial wombs, utilizing data analytics and biotechnology to cater to each premature infant's unique developmental needs. Additionally, with the ethical intricacies surrounding artificial womb technology, startups can offer consulting services to aid research institutions and corporations in navigating regulatory and ethical guidelines while pushing the boundaries of this technology.
For corporate innovators: Pharmaceutical companies and hospital networks can establish collaborative platforms with research institutions and startups could propel the development and commercialization of artificial womb technologies. Corporations could also venture into creating high-fidelity training simulators for medical professionals to practice the transfer of premature infants to artificial wombs, ensuring smooth transitions and minimizing risks. Partnerships with biotech firms for advanced monitoring systems providing optimal fetal development could also be explored.
For public sector innovators: Government agencies could proactively develop a robust regulatory framework ensuring the safe and ethical deployment of artificial womb technology. Engaging in dialogue with ethicists, medical professionals, and the public to address concerns and shape policy may be crucial. Public-private research grants could encourage collaborative research between public institutions and private entities on artificial womb technology, focusing on reducing the incidence of preterm births and improving neonatal care.
Outside curiosities
Startup Humane’s wearable AI pin, supposedly designed to replace smartphones, was featured by models during the Paris Fashion Week. (This reminds us of the Star Trek computer brooch.)
Aston Martin has released limited edition orange versions of every model since 2010 (the entire collection is worth USD $500,000).
AR One Sans is a new font designed exclusively for augmented reality environments.
This photography feature from Google Pixel 8 ensures everyone has their best angle in a group shot (this can potentially save friendships 🤯).
More from Quantumrun
Read more daily trend reporting on Quantumrun.com
Subscribe to the Quantumrun Trends Platform (free for premium newsletter subscribers).
Corporate readers can review our Trend Intelligence Platform
Email us at contact@quantumrun.com with questions or feedback.
Finally, share your thoughts in the Substack comments below. We love hearing from you!
David Tal, Quantumrun President: Interested in collaborating with the Quantumrun Foresight team? Learn more about us here.
See you in The Futures,
Quantumrun





