The Futures - No. 47
Freefalling battery prices making EVs affordable / AI drives corporate downsizing spree / Scar-free skin reconstruction
In this issue
The Quantumrun team shares actionable trend insights on how collapsing battery technology prices could drive electric vehicle (EV) affordability, businesses replacing human labor with AI, Google’s new attempt to fight off AI content spam, and breakthrough 3D-printed skin reconstruction.
Future signals to watch
Watch this video of Starship launching into space and landing safely back to Earth. A significant advancement for SpaceX and for humanity’s progress as a spacefaring civilization. Weighing in at 5,000 tons, Starship is the largest and most powerful spacecraft to ever take flight.
Once the Starship line of rockets/spacecrafts transitions into mass production by the early 2030s, the cost of space missions will fall dramatically, making a whole new series of space-based industries possible.
Google is updating its search results policies to tackle evolving spammy practices and low-quality, automated (and increasingly AI-generated) content. These measures aim to improve the quality of search results by addressing sophisticated AI content generation methods and the misuse of reputable sites or expired domains to manipulate rankings.
Gene-edited pigs with immunity to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome—a disease costing global agriculture billions—are poised to be the first CRISPR-modified animals in mass meat production.
What happens when you combine OpenAI tech with a humanoid robot? See for yourself.
Researchers analyzed 23 years’ worth of dengue data in Vietnam. They discovered that the spread of the disease is influenced by urban infrastructure, human mobility, and temperature. This challenges the notion that it's purely an urban disease and highlights the role of climate change in its expansion.
A study in Nature reveals that groundwater levels in 71% of the world's aquifers are declining due to excessive extraction, particularly in dry climates.
Most companies from the UK's largest four-day working week trial in 2022 continued with the reduced schedule, reporting improved revenue, worker well-being, and no loss in productivity.
An analysis reveals that mathematician cliques, primarily in China and Saudi Arabia, inflate citation counts through low-quality papers, affecting university rankings.
University of Southern California researchers have achieved a milestone in synthetic biology by creating a partially synthetic genome for spreading earth moss, showcasing its potential as a bio-factory for medicines and demonstrating a step towards fully artificial plant genomes.
Researchers have achieved a groundbreaking advancement by 3D-printing multi-layered, living skin directly onto rats' injuries for scar-free injury repair, potentially including hair regrowth. This innovation by Pennsylvania State University could revolutionize reconstructive surgery for the face and head, addressing challenges like scarring, hair loss, and graft failure.
Culturally // Trending
YouTube → Fallout // X → Oscars Kenergy // Reddit → Google’s newest quantum computer // TikTok → Hopecore // Instagram → Coquette Girl // Spotify → “Holy Smokes”
🔋 Battery prices are falling so fast that they might soon make EVs affordable
A January 2024 report by the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) shows that battery sales have been doubling every two to three years, with electric vehicles (EVs) fueling this growth. Falling costs (99% drop over three decades) and increasing energy storage capacity have made batteries more affordable and effective. This trend has led to major battery manufacturers like CATL and BYD planning to cut prices by half in 2024.
China-based CATL is optimizing production to reduce the cost of its Vehicle Designated Architecture (VDA)-compliant lithium iron phosphate battery cells to around $56.47 per kWh. This shift could cut battery manufacturing costs by half within a year, saving EV manufacturers more than $3,000 per vehicle.
As battery technology becomes more affordable, it's unlocking larger applications like increasing their use in trucks, energy storage, ships, and airplanes. By 2030, RMI predicts that batteries will transform industries, reducing reliance on fossil fuels for transportation and electricity production.
Global battery sales by sector, GWh/y

However, despite the significant reduction in battery costs, the transition to electric cars faces hurdles, such as the availability of fast-charging infrastructure and consumer skepticism due to previous price inconsistencies. Even large automakers remain cautious, such as General Motors, which cut its EV production in half in 2024. Nonetheless, the relentless advances in battery technology will, at the very least, enable a broader group of customers to consider owning an EV.
Goldman Sachs predicts a 40% decrease in battery pack prices by 2024, followed by an additional 10% drop by 2025-2026. This could make EVs more cost-competitive with gasoline-fueled cars. Moreover, lithium hydroxide, a crucial component in EV batteries, has seen a price fluctuation, rising sharply in late 2021 and 2022 but declining since early 2023, with the trend continuing as of March 2024.
Actionable trend insights as technology drives a battery price collapse
For entrepreneurs
Home developers and contractors can explore new residential installation services for homebuyers who want to install more affordable home battery packs that better integrate with local microgrids, solar roof installations, or future EV purchases.
Depending on the country and the dominant EV brands in the domestic market, entrepreneurs can explore developing subscription-based battery-swapping services for EVs. This model would enable EV owners to quickly exchange depleted batteries for fully charged ones at convenient locations, addressing concerns about charging infrastructure and range anxiety.
In other markets, the demand for creating or expanding businesses related to installing charging stations and specialized EV repair shop locations will continue throughout the 2020s.
For corporate innovators
Companies can integrate solar and energy storage solutions into their facilities to optimize energy usage and reduce costs. For instance, manufacturing facilities can implement large-scale battery systems to store excess energy during off-peak hours and use it during peak demand periods, minimizing electricity expenses and reducing their reliance on the grid.
Logistics companies can invest in electric delivery vans or trucks equipped with next-generation batteries, which will enable them to benefit from lower fuel costs and reduced maintenance expenses over the vehicle's lifetime. Moreover, EVs offer operational advantages, such as quieter operation, smoother acceleration, and fewer moving parts, leading to decreased downtime and increased productivity.
For public sector innovators
Government agencies at all levels can collectively invest (at reduced rates) in grid-scale energy storage projects to support the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid. By deploying large-scale battery systems, public utilities can mitigate solar and wind energy's intermittency, enhance grid stability, and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Furthermore, as battery prices continue to fall, making public infrastructure resilience investments will become easier to justify. For instance, governments can invest in community microgrid projects—powered by renewable energy sources and supported by affordable battery storage systems—that can provide critical backup during extreme weather events, natural disasters, or grid outages.
Trending research reports from the World Wide Web
According to a Royal Institute of British Architects report, 41% of UK architects incorporate AI into their projects.
Based on Rutgers University's survey, 70% of US workers express concerns about AI in HR decision-making, while 30% fear job elimination due to AI.
KPMG discusses the future of the global legal workforce and thinks remote work has shifted from a rarity to a permanent fixture in the law sector, with leading organizations adopting policies to capitalize on global recruitment opportunities.
MIT Technology Review examines several reasons why chatbot search is a bad idea, including AI's tendency to invent complex information and pass it off as authoritative.
Deloitte discusses advancements in e-government initiatives and how they can help address constituent needs.
💼 Companies point to AI as the reason for headcount downsizing
In February 2024, Sweden-based fintech company Klarna announced that their AI assistant, powered by OpenAI, handled 2.3 million conversations, which represents two-thirds of the company's customer service interactions since its launch. This AI system is credited with performing the work of 700 full-time agents, improving customer satisfaction through faster resolution times and reducing repeat inquiries by 25%. Moreover, the chatbot is projected to contribute a $40 million profit this year. In 2022, the company laid off 10% of its workforce (or 700 employees), leading some media outlets to guess that these laid-off employees were the agents the AI assistant replaced.
Klarna is not alone in leveraging AI for operational efficiency and cost reduction. Across industries, firms like UPS and BlackRock have attributed significant layoffs and operational changes to adopting AI technologies. JPMorgan says its AI cash flow software cut human work by nearly 90%. These developments are part of a larger trend where AI's role in the workforce is evolving from simple task automation to more complex problem-solving and customer interaction roles.
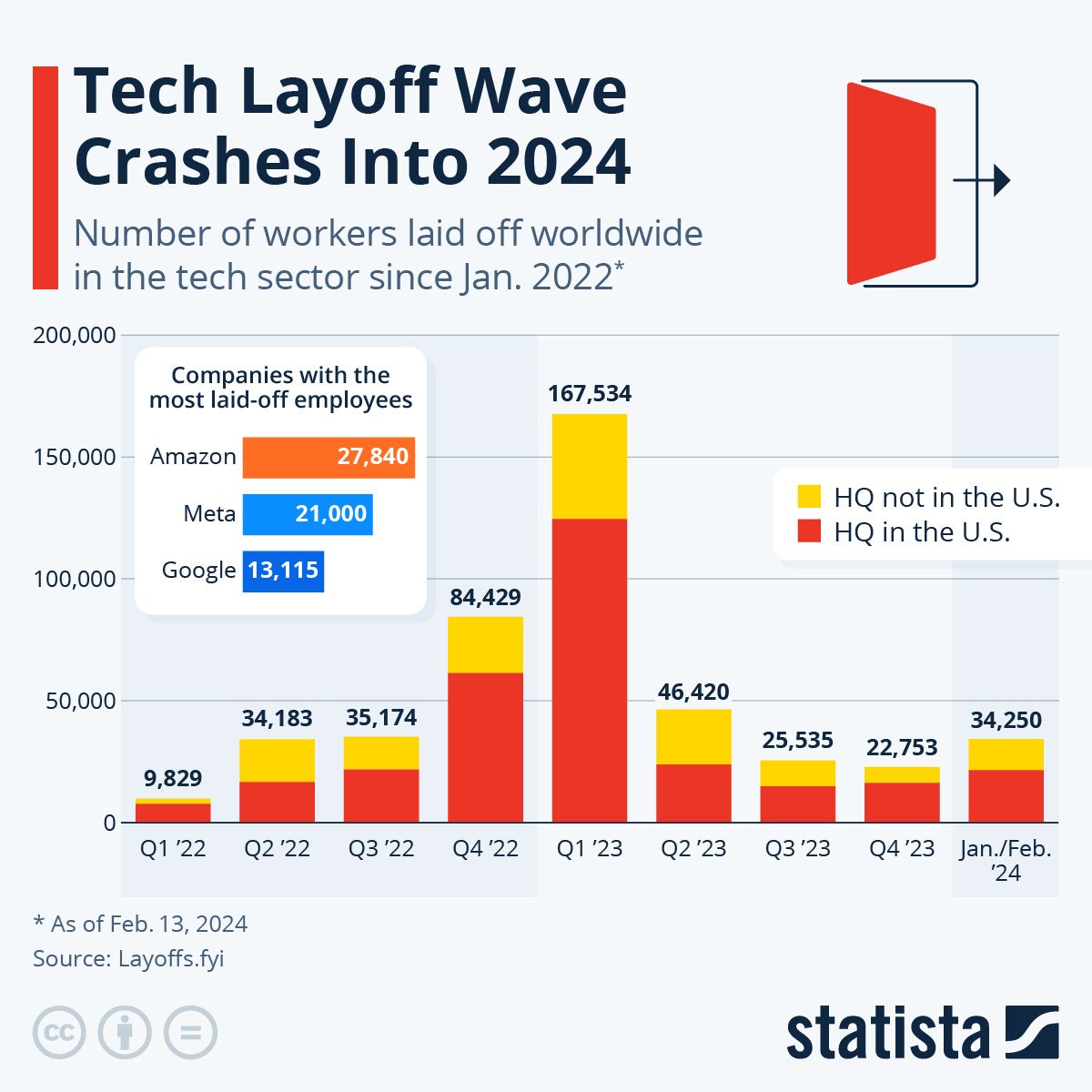
As AI advances, it's projected to lead to more job displacements. For instance, the outplacement firm Challenger, Gray & Christmas noted that over 4,600 job cuts announced by US companies since May 2023 were related to AI, indicating a significant underestimation of the technology's impact on employment.
The implications of this shift toward AI-driven operations suggest a transformation in the nature of work and the skills required in the future workforce. While AI brings efficiency and productivity gains, it also needs a reevaluation of workforce development strategies. This entails investing in retraining and upskilling programs to prepare workers for the evolving demands of the job market. Moreover, as AI applications become more widespread, the need for thoughtful discourse on these technologies' ethical, social, and economic impacts becomes increasingly critical.
Actionable trend insights as companies continue to downsize due to AI
For entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs can develop consultancies or digital platforms tailored for small and mid-sized companies looking to optimize their operations and workforce in response to AI advancements. Such services could leverage AI to analyze job roles, spot redundant employee skills, propose upskilling opportunities, while also identifying automation opportunities—all with the goal of modernizing businesses and (where possible) preemptively adapting their workforce rather than downsizing.
For corporate innovators
More corporations can explore the creation of departments devoted to researching automation opportunities, or roles like Chief Automation Officer, to identify and lead the implementation of programs that utilize AI or robotic automation into company workflows.
Firms can develop internal AI upskilling academies that teach employees the skills to work alongside AI technologies. A practical application could be training customer service representatives to manage and improve AI chatbots based on insights gathered from customer interactions. This would move their roles up the value chain from direct service to strategic enhancement of customer experience tools.
For public sector innovators
Governments can invest in sector-specific AI impact assessments to inform policy and economic planning. For instance, if an impact assessment reveals that workers in the transportation and logistics sectors are at high risk due to autonomous vehicle technology, governments could encourage public-private partnerships in transportation education and adjust infrastructure spending to support a transition to new employment opportunities.
Municipalities can simulate different urban development scenarios to assess AI's potential impacts on employment in various sectors and plan proactive interventions. Using these insights, governments can work with community colleges and vocational schools to tailor educational programs that prepare the local and regional workforce for AI-driven jobs.
Outside curiosities
Three million World of Warcraft (WoW) fans in China lose access to the game after publisher Activision Blizzard decides not to renew its deal with Chinese distributor NetEase.
Who was even going to watch Coyote vs Acme?
What people will most likely watch is Netflix’s stream of a Jake Paul versus Mike Tyson fight in July.
Hollywood crews say that they’re still not getting enough work post-strikes.
This is … too much tech.
More from Quantumrun
Read more daily trend reporting on Quantumrun.com
Subscribe to the Quantumrun Trends Platform (free for premium newsletter subscribers).
Corporate readers can review our Trend Intelligence Platform
Email us at contact@quantumrun.com with questions or feedback.
Finally, share your thoughts in the Substack comments below. We love hearing from you!
Interested in collaborating with the Quantumrun Foresight team? Learn more about us here.
See you in The Futures,
Quantumrun