In this issue
The Quantumrun team shares actionable trend insights about young people co-buying homes, precision attack drones becoming a war staple, NVIDIA’s big push into the humanoid robot market, and the rise of AI musicians.
Future signals to watch
NVIDIA launched its Project GR00T, teaching humanoid robots to understand multimodal input, including through language, video, and observing humans. The company uses its Jetson Thor chips, which are designed to power AI-driven machines.
German intelligence has analyzed the military threat posed by Russia, forecasting potential attacks on NATO member countries starting in 2026.
Saudi Arabia is planning to pour USD $40 billion into artificial intelligence (AI) investments in its bid to become the Silicon Valley of the Middle East.
Startup Interlune plans to extract helium-3 from the Moon's surface and bring it back to Earth. Helium-3 is an isotope that does not form on Earth but is critical to advancing superconducting quantum computers.
The Chinese electric vehicle (EV) dominance has gotten so strong that even Japanese rivals Honda and Nissan have joined forces to develop EV technology.
Astronomers using the James Webb and Hubble space telescopes have deepened the Hubble Tension problem by confirming that the universe's expansion speed varies, questioning our understanding of the universe.
New research indicates that ski regions in Australia and New Zealand are expected to soon experience significantly reduced snowfall due to climate change.
Startup Suno released this clip of a realistic blues song created by its AI model. The startup is just one of the companies (like Google and YouTube) aggressively investing in AI audio, sparking more debates on copyright infringement and human musicians losing to automation.
On the flip side, musicians are attempting to regain control by sharing their unreleased music with fans for a monthly subscription.
Culturally // Trending
YouTube → Beetlejuice Beetlejuice // X → Late Night with the Devil AI scandal // Reddit → This Walmart “Easter Bunny” // TikTok → The notorious Duolingo memes // Instagram → Maximalism // Spotify → “We can’t be friends (wait for your love)”
🏠 Millennials and Gen Z turn to communal home buying
Younger generations struggling with housing affordability are increasingly buying homes with peers and family members. Recent years have seen an upsurge in property prices, fueled by limited housing stock, increasing interest rates, and a significant rise in home equity. As reported by the US Federal Reserve, between early 2020 and the third quarter of 2023, US households saw their home equity soar by $12.6 trillion, culminating in a staggering total of $32.6 trillion.
At the same time, novel financial arrangements like home-equity-sharing agreements have gained traction, offering homeowners a pathway to liquidate a portion of their equity without traditional borrowing. While such deals provide immediate financial relief, they often come with long-term commitments and potential risks, predominantly favoring investors who are betting on continuous market appreciation.
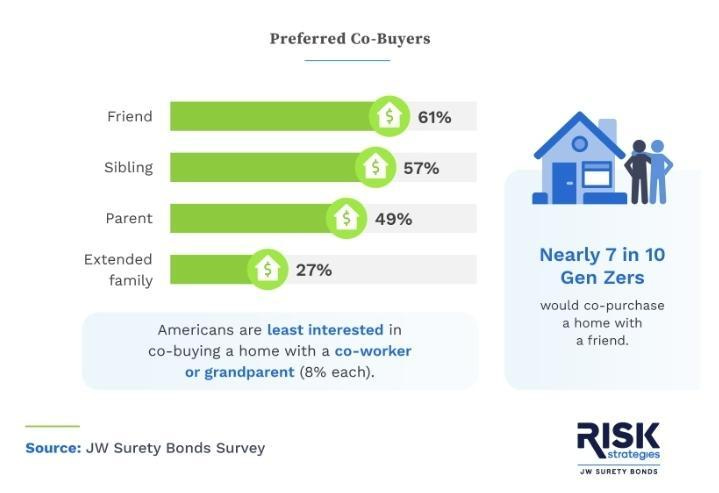
Parallel to these financial innovations, communal home buying is gaining ground among Millennials and Gen Zers due to the prohibitive costs of individual homeownership and a desire to mitigate isolation. Reports from ATTOM Data Solutions and findings by Redfin highlight a 771% increase in co-home buying among Americans from 2014 to 2021. In addition, 15% of prospective buyers are considering shared mortgages with non-spousal roommates.
Meanwhile, startups like BotBuilt are capitalizing on these shifts by offering technological solutions to the housing crisis. BotBuilt employs robotics to construct home framing, significantly lowering construction costs and timelines. The company's approach addresses the housing market's supply-side constraints and the demand for more affordable living arrangements.
Actionable trend insights as younger generations adopt communal home buying:
For entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs could establish a cooperative real estate agency specializing in communal properties, offering a full suite of services tailored to the unique needs of communal buyers.
Mid-sized property investors can explore organizing and facilitating group investments in underutilized commercial properties, converting them into mixed-use developments that combine residential living with communal workspaces, retail, and green spaces.
Entrepreneurs can also develop a business model that pairs interested buyers with environmentally friendly properties, incorporating green technologies such as solar panels, shared electric vehicle charging stations, and communal gardens.
For corporate innovators
Construction, real estate, and technology companies can develop modular housing units designed for communal living. These units can be easily assembled, expanded, or reconfigured to meet the changing needs of a home-buying group. By using advanced materials and smart home technologies, these units can offer flexibility, scalability, and efficiency, catering to the dynamic nature of communal living arrangements.
Large employers could invest in employee housing co-ops as part of their benefits package. These co-ops could feature amenities tailored to the preferences of the employee community, such as shared offices, recreational facilities, and childcare centers.
For public sector innovators
Governments can develop and implement zoning reforms and incentives to promote and support communal home buying and co-living developments. Such reforms could include offering tax incentives or building requirements for developers to create more multi-family dwellings that communal buyers can adapt into communal living spaces.
Government agencies can invest in communal living resource centers that provide legal, financial, and logistical assistance to groups interested in forming communal living arrangements. For example, a city could repurpose unused public buildings into communal living pilot projects, offering them to co-ownership groups at below-market rates.
Trending research reports from the World Wide Web
More than half of companies in the UK, US, Canada, Australia, and Germany employ at least three generations, and 79% of workers are open to working with the youngest generation—Generation Alpha.
According to a recent Deloitte report, a mere 3% of respondents believe their organizations excel at leveraging the value generated by employees.
Based on the 2024 Edelman Trust Barometer report, developing nations have more trust in their businesses, governments, and media institutions than developed countries. (The UK has become one of the least-trusting countries).
Technology leaders are 12% more inclined than business leaders to use sales of new digital products as a key performance indicator and 7% more likely to concentrate on sales via new digital platforms.
🛰️ Military precision weapons shift control to soldiers
Precision weaponry in military operations has evolved beyond the capabilities introduced in the late 20th century. Initially, the US led the integration of information technologies with military hardware, resulting in munitions delivery with unparalleled accuracy. This shift from broad area bombardment to precise strikes minimized collateral damage and increased the efficacy of targeted attacks.
However, the democratization of these advanced technologies now permits individual soldiers and smaller units to autonomously deploy precision-guided systems. This shift can be seen in the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine, where Ukrainian drones have been adapted for strategic roles, from naval disruption using explosive-laden jet skis to infantry engagement with grenade-dropping drones.
Ukraine and Russia have been strategically deploying low-cost drones to infiltrate enemy territory and disrupt troops for as low as USD $400 each. The US has taken note of this strategy and is planning to mass-produce low-cost, AI-enabled drones through its Replicator program in preparation for future conflict with China over Taiwan. In addition, in February 2024, the UK and the US announced they would supply Ukraine with thousands of AI-enabled unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that target adversary positions through collective intelligence and coordination.
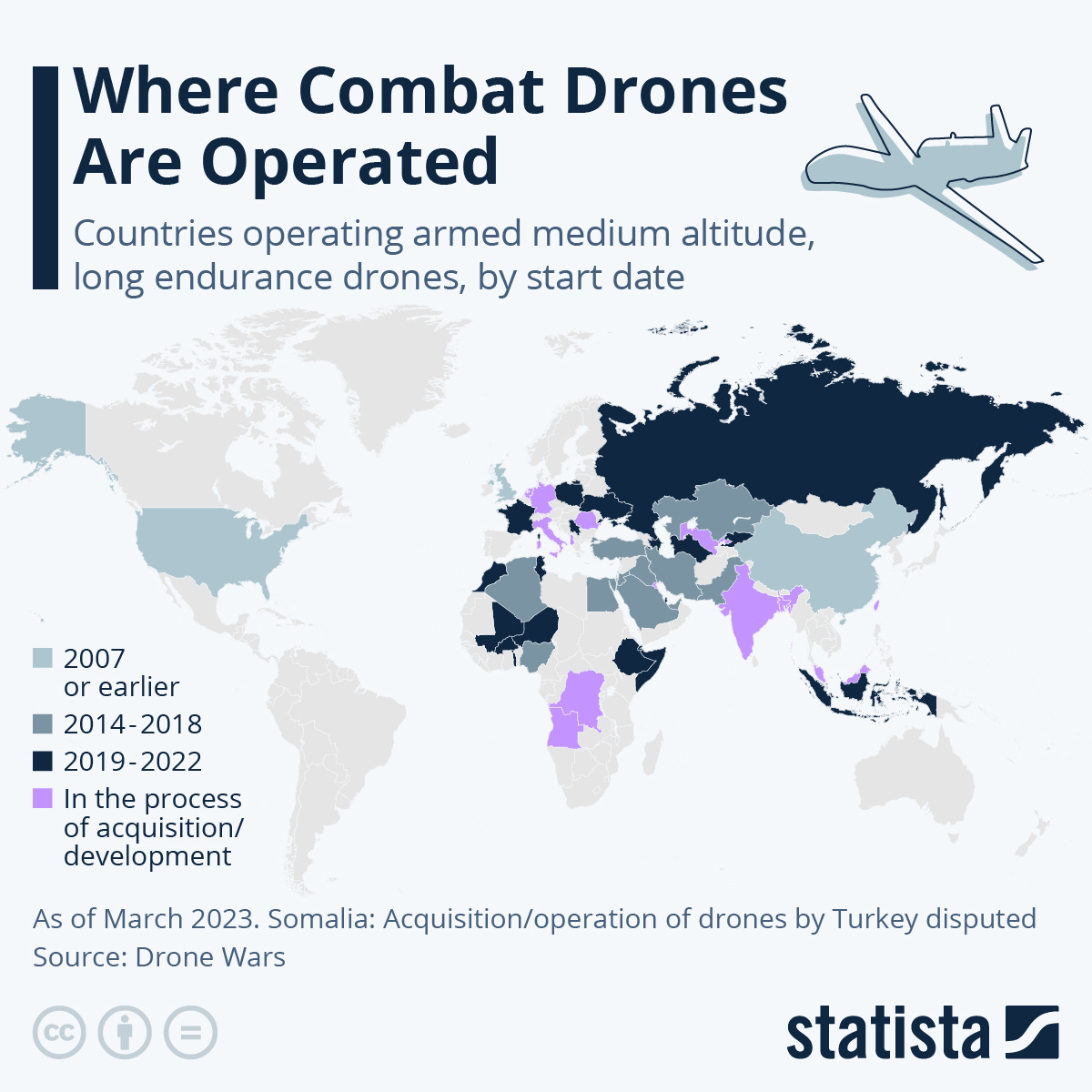
This evolution in precision warfare technology is not isolated. A growing number of states, such as Armenia, China, South Korea, and the US, are announcing drone swarm programs. These swarms aim to enhance battlefield decision-making, reduce costs, and minimize human casualties. However, they also raise concerns about undermining international security and human rights.
Meanwhile, using drones (like American-made Phoenix Ghost) for mid-range infrastructure strikes and deep enemy territory missions signifies a move towards a more granular level of warfare, where the precision and reach of attacks are no longer the responsibility of a centralized military command. These technologies enable greater autonomy and adaptability on the battlefield and will require new countermeasures.
In addition, the impact on enemy infrastructure and revenue streams blends traditional military objectives with strategic economic disruption. As these technologies develop, wars may transition into creative, hyper-targeted disruptions rather than depend on sheer numbers and brute force.
Actionable trend insights as more countries adopt precision and strategic warfare
For public sector innovators
Defense agencies can establish drone swarm innovation hubs to develop, test, and ethically deploy autonomous systems. These hubs, partnering with academia, industry, and ethical oversight committees, could focus on the dual-use applications of precise drone technology in disaster response, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure inspection.
Governments may consider applying additional safeguards and security clearances upon domestic drone manufacturers to ensure critical technology is not exported to bad actors. Likewise, government subsidy programs may be applied to support domestic drone manufacturing so that drone swarms can be produced at scale to defend against future threats from hostile nations.
Militaries can develop advanced infantry training programs that use augmented and virtual reality (VR) to simulate conflict scenarios involving precision and strategic warfare technologies. For instance, a VR training module could simulate an environment where soldiers must neutralize drones targeting critical infrastructure, teaching them how to make quick real-time decisions.
Outside curiosities
It seems the era of sensationalized, extravagant YouTube videos popularized by Mr. Beast is coming to an end.
Employer branding has become a TikTok game, with companies aiming to establish virality and brand reputation on the video platform. (If you've ever come across a Duolingo meme of its intimidating owl mascot, you know they're winning at this strategy.)
Speaking of branding, NVIDIA joined the Stanley cup/tumbler hype.
Wind turbines, but make it art.
Earables, but make it fashion.
More from Quantumrun
Read more daily trend reporting on Quantumrun.com
Subscribe to the Quantumrun Trends Platform (free for premium newsletter subscribers).
Corporate readers can review our Trend Intelligence Platform
Email us at contact@quantumrun.com with questions or feedback.
Finally, share your thoughts in the Substack comments below. We love hearing from you!
David Tal, Quantumrun President: Interested in collaborating with the Quantumrun Foresight team? Learn more about us here.
See you in The Futures,
Quantumrun