The Futures - No. 64
New global manufacturing hotspots / AI redefining productivity / Successful robotic surgeries
Artist: Quantumrun via DALL-E
In this issue
The Quantumrun team shares actionable trend insights about global manufacturing continuing to shift away from China, AI tools redefining productivity, the world’s largest solar farm, and Saudi Arabia’s high robotic surgery success rate.
Future signals to watch
The world’s largest solar farm in Xinjiang, spanning 33,000 acres and generating 3.5 gigawatts, is now connected to China’s grid. This solar farm will produce about 6.09 billion kWh annually, enough to power 2.03 million EVs, and is part of China's 455 GW wind and solar megabase project.
Berkeley researchers have discovered a new method to direct specific DNA insertions, removals, and inversions, enhancing genome design tools beyond CRISPR and RNA interference.
TDK announced a breakthrough in developing a material for solid-state batteries with an energy density 100 times greater than their conventional batteries, promising significantly higher performance for wearable devices.
Legendary sportscaster Al Michaels will deliver daily, personalized recaps of the Paris Olympics on Peacock via an AI-generated voice, providing custom coverage based on user preferences for sports and highlights.
Berkeley researchers successfully tested their 3D printing technology, SpaceCAL, in suborbital space during the Virgin Galactic 07 mission, autonomously printing four test parts in 140 seconds.
Austrian startup Cellectric Biosciences is developing an electromagnetic platform to isolate pathogens from human samples, enabling blood sepsis diagnosis in less than four hours.
Google Translate is using the PaLM 2 large language model to add 110 new languages, marking its largest expansion ever and continuing to break down language barriers.
Saudi Arabia’s King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre has achieved a 98% survival rate in 400 robotic cardiac surgeries since February 2019, marking a major milestone. This success solidifies its position as a global leader in robotic cardiac care and demonstrates significant improvements in patient outcomes compared to traditional methods.
Forward this email to a friend and help The Futures reach a wider audience :)
Culturally // Trending
YouTube → Agatha All Along // X → The end of the Cartoon Network Era // Reddit → Sydney’s newest metro // TikTok → These track and field Olympic uniforms // Instagram → JCrew releasing a The Bear outfit capsule // Spotify → “Cowboys Cry Too”
🏭 Global manufacturing continues to shift away from China
Since 2018, Western countries have been moving production out of China due to trade tensions initiated by then-president Donald Trump. Now, Chinese companies are also seeking alternatives due to geopolitical risks and rising costs. Many China-based manufacturers are exploring overseas production to mitigate supply chain challenges and political risks. While India is expected to benefit significantly, much of this manufacturing shift is directed toward Southeast Asian countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia.
Southeast Asia manufacturing value added
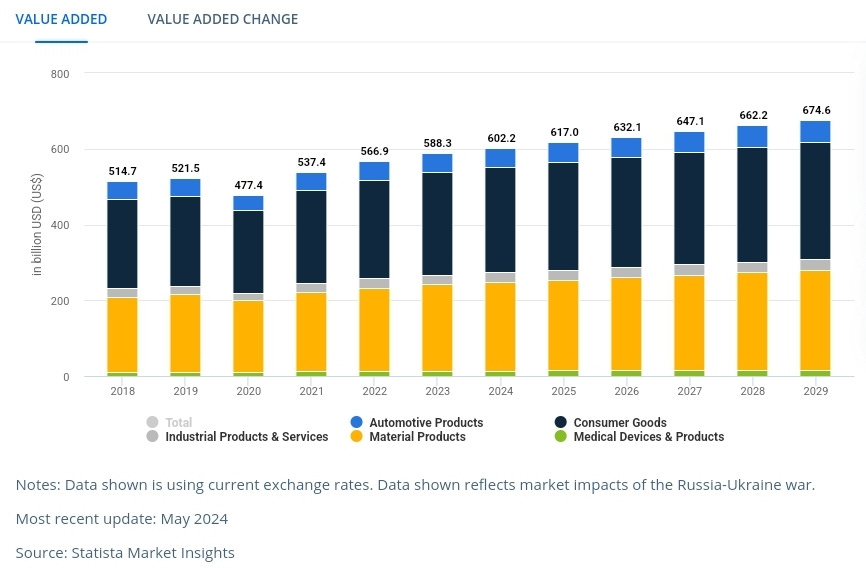
Vietnam's focus on high-end manufacturing, supported by its significant STEM graduate workforce, positions it as a critical node in the regional supply chain. Indonesia, with its large population and expanding infrastructure, complements this next-gen supply chain by handling lower-end manufacturing. This regional integration is attracting investments from the US and Japan. As these regions continue to develop their infrastructure and labor forces, they are set to play an increasingly central role in global manufacturing.
Meanwhile, North America is also becoming an attractive manufacturing hub due to its extensive infrastructure and substantial consumer base, particularly in the US and Mexico. Mexico, with its youthful population, is increasingly integrated into the North American production system, presenting significant opportunities for growth. As the US continues to restrict technology exports and adopts nearshoring, Mexico is anticipated to benefit the most from this partnership. This regional synergy is expected to capture a considerable share of the manufacturing sector as companies seek stable and efficient production environments.
The US itself is seeing a manufacturing renaissance, with investments in new factories hitting a record high of USD $225 billion in February 2024. This boom is primarily driven by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), and the CHIPS and Science Act, which have boosted domestic semiconductor, electric vehicle battery, and wind turbine production.
Actionable trend insights as global manufacturing continues to shift away from China:
For entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs specializing in physical products should explore niche labor markets within the emerging manufacturing hubs. For instance, Vietnam's focus on high-end manufacturing presents opportunities in technology and electronics, while Indonesia's capabilities in lower-end manufacturing could benefit consumer goods production.
Entrepreneurs can form strategic partnerships with local manufacturers and suppliers to tap into the existing infrastructure and networks. This can help reduce initial setup costs and mitigate risks associated with new market entry.
For corporate innovators
Companies can negotiate partnerships with local governments to make co-investments in local infrastructure development in emerging markets to ensure reliable and efficient production. These collaborations with local governments can lead to building the necessary facilities and transportation networks needed to best utilize locally available labor.
In North America, where nearshoring is being prioritized, corporations can embrace Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things, automation, and artificial intelligence, to enhance efficiency and competitiveness. This is particularly crucial in markets like the US where manufacturing is driven by technological advancements.
For public sector innovators
Governments in emerging markets can offer targeted incentives (e.g., tax breaks, grants, and low-interest loans) to attract foreign direct investments in industries where their domestic labor market has a competitive advantage. This is particularly effective for developing regions looking to establish themselves as manufacturing hubs.
Federal governments can prioritize infrastructure development, including transportation, utilities, and digital connectivity. Reliable infrastructure is critical for efficient manufacturing operations and attracting large-scale foreign investments.
Trending research reports from the World Wide Web
ARK Invest's research predicts that AI agents will enable nearly $9 trillion in global private consumption by 2030, influencing 25% of online consumer goods and services sales.
The IEA's 2023 World Energy Outlook reports that China's economic growth is slowing, but its energy demand continues to rise, with per capita consumption now surpassing Europe's, driven by a 489% increase from 2001 to 2021.
While the media often suggests AI is rapidly taking over, most companies are still in the early stages of adoption, with only 9.8% feeling they are leading in 2024, down from 13.4% in 2023.
According to the LinkedIn Workplace Learning Report 2024, Gen Z workers are the most interested in learning to progress their career.
A survey across the US, UK, Australia, and Canada discovered that Americans shop the most on Chinese marketplaces like Shein, AliExpress, and Temu.
📈 AI tools are making economists rethink productivity metrics
With the ongoing debate on artificial intelligence (AI)’s potential to automate (and replace) jobs, economists are starting to revisit traditional concepts of productivity. For instance, Erik Brynjolfsson from Stanford University is optimistic, noting that AI has the potential to enhance efficiency across various sectors.
An example is Abercrombie & Fitch using AI for generating product descriptions, streamlining their processes and reducing workload. Meanwhile, Batesville Tool & Die in Indiana turned to AI-driven robots to mimic human workers and vision systems to enhance their manufacturing processes, exemplifying how robotics can fill labor gaps and boost productivity.
The shift in productivity paradigms is driven by AI's capability to automate mundane tasks and enable workers to focus on higher-value activities. For example, Ben & Jerry's employs AI-powered cameras in freezers to manage inventory effectively, resulting in a 13% increase in sales.
Despite these benefits, not all economists are convinced of AI's immediate impact on productivity. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell has expressed skepticism about AI's short-term productivity benefits, though he acknowledges its potential in the long run. This debate reflects a broader uncertainty about how quickly AI can transform various industries and whether these gains will be reflected in productivity statistics.
According to a study by Erik Brynjolfsson and colleagues, AI tools significantly increased productivity in a call center by 14%, with the greatest gains seen among less experienced workers. This suggests that AI could democratize productivity enhancements, allowing companies to achieve more with less experienced staff.
The US, with its flexible labor market, may adapt more quickly to AI-driven changes compared to China, where the emphasis on social stability may hinder rapid workforce transitions, potentially reducing AI's productivity benefits. However, the full potential of AI in boosting productivity will depend on how quickly businesses can integrate these technologies and how policymakers address the challenges of workforce displacement and inequality.
Actionable trend insights as AI tools boost productivity:
For corporate innovators
Companies can identify key areas where task automation can have the most impact, working with AI and robotics vendors to develop or customize solutions that fit their specific needs. They can train employees on how to use the new AI and robotics tools effectively and track productivity improvements to measure the return on investment.
Likewise, companies can implement AI-driven wellness programs that monitor employee health metrics, suggest personalized wellness plans, and provide mental health support. AI can analyze data from wearable devices and employee surveys to create customized health and wellness recommendations, reducing stress and increasing productivity.
For public sector innovators
Federal ministries of economic development, potentially in partnership with central banks, can fund studies that explore modernizing how nations measure productivity in response to emerging automation technologies.
Governments at all levels can use AI to streamline and improve the efficiency of public services, such as permit processing, citizen inquiries, and resource allocation. For example, AI can automate the processing of permit applications, reducing wait times and improving accuracy.
Outside curiosities
Nike and Hyperice to collaborate on launching a shoe that acts like compression leggings for athletes.
The US beauty industry is now required to disclose ingredients considered as “secret” or proprietary.
Poe, an AI chatbot platform owned by Quora, offers users downloadable HTML files of articles from paywalled journalistic outlets.
X (formerly Twitter) is considering reintroducing a downvote feature for replies to help rank them in a thread. (X is saying it’s not trying to be Reddit.)
More from Quantumrun
Read more daily trend reporting on Quantumrun.com
Subscribe to the Quantumrun Trends Platform (free for premium newsletter subscribers).
Corporate readers can review our Trend Intelligence Platform
Email us at contact@quantumrun.com with questions or feedback.
Finally, share your thoughts in the Substack comments below. We love hearing from you!
Interested in collaborating with the Quantumrun Foresight team? Learn more about us here.
See you in The Futures,
Quantumrun





How will the shift of global manufacturing away from China impact international trade dynamics and local economies in emerging manufacturing hubs?