In this issue
The Quantumrun team shares actionable trend insights about innovations in water desalination potentially solving the world’s growing water availability crisis, humanoid robots giving companies a labor advantage against unions, a tooth-growing drug by Japanese scientists, and the US' ambitious plans to commercialize nuclear fusion.
Future signals to watch
The US government plans to build its first nuclear fusion plant within 10 years to hit its target of a carbon-free energy sector by 2035.
Toregem Biopharma has developed a drug that promotes tooth regrowth (aiming for human trials by 2024), with a market launch by 2030.
AST Space Mobile announced that its Blue Walker 3 test satellite, having been in orbit for a year, recently transmitted its first 5G phone call to a regular smartphone in an area lacking cellular coverage.
The SMART Tire Company has commercialized NASA's initial airless tire technology to launch SMART METL tires for bicycles that aim to provide a smooth ride and longevity. (The era of flat tires may finally come to an end.)
Scientists discovered that a specific therapy can precisely target and manage unruly immune responses in mice and non-human primates, offering a promising avenue for treating autoimmune diseases.
Scientists at the University of California San Diego have transformed ordinary earbuds into sophisticated devices capable of capturing the brain's electrical signals. (Basically, a potential future alternative to brain implants.)
This demonstration shows the whole new world that ChatGPT-4 Vision has opened.
Desalination is set to become insanely cheap, potentially solving future water access issues

The cost of desalination—turning saltwater into drinkable water—is falling dramatically. This cost-effectiveness is illustrated in water-scarce countries like Israel, where 25 percent of its domestic water supply comes from desalination, particularly from the Sorek B plant, which produces water at a low cost. Likewise, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is another testament to this technology's potential, with desalinated water constituting the entire municipal supply.
A comparison between 2012 and 2022 reveals a dramatic reduction in the cost of desalinating water, falling from $0.75 per cubic meter in 2012 (in the US) to a mere $0.41 in 2022 (-45%). This trend showcases a significant increase in water abundance due to desalination, a 10.22 percent compound annual growth rate despite the growing global population. Continued investments in desalination tech will see further cost reductions over the decades ahead.
Water desalination process in the US

For instance, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Shanghai Jiao Tong University engineers are pushing this technology forward by developing a solar desalination system that could produce freshwater that is cheaper than tap water. Inspired by natural ocean movements and powered by sunlight, this system heats saltwater, causing the water to evaporate and leave behind salt. The vapor then condenses into clean, drinkable water.
The researchers improved the design to prevent salt clogging and enhance water production and salt rejection rates, making this iteration more efficient and reliable. Scaling up this and similar innovations could provide an affordable, passive method to meet a small family's daily water needs or help off-grid coastal communities, possibly even at a cost lower than current tap water production.
Actionable trend insights as water desalination becomes increasingly cheap
For entrepreneurs: Desalination plants are capital-intensive enterprises that fall outside the means of most entrepreneurs. However, building software and hardware to make desalination and water recycling more efficient and selling these innovations to state-backed desalination firms and agencies remains viable.
For corporate innovators: Companies in water-intensive industries, like agriculture, beverage, or manufacturing, can incorporate desalination technologies in their operations. Similarly, corporations could also use desalination tech to recycle and treat industrial wastewater. Such investments could significantly reduce their reliance on external water supplies, ensure a consistent supply, and improve their corporate sustainability efforts. Corporations can also invest in startups or established companies pioneering new desalination technologies.
For public sector innovators: Governments worldwide can explore new public-private partnerships to dramatically build out the number of next-generation desalination plants and improve water infrastructure. Government utilities agencies can also provide a framework for sharing the risks and benefits of large-scale desalination projects, including grants, tax breaks, low-interest loans, and other subsidies to encourage private sector participation. These partnerships could help rapidly expand access to clean water in water-scarce regions, as well as reduce agricultural costs.
Trending research reports from the World Wide Web
An interesting discussion by venture capital Andreessen Horowitz on why the remarkable rate of generative AI adoption makes this technology not only financially sustainable but also capable of driving market transformations comparable to the microchip and the Internet.
The New York Magazine discusses why OpenAI CEO Sam Altman can be the next century-defining disruptor, similar to nuclear bomb creator J. Robert Oppenheimer.
According to a London School of Economics and Political Science survey, over three-quarters of participants employ AI in one or more stages of the news value chain, including news collection, creation, and dissemination.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are becoming a dead market, according to crypto and online gambling platform dappGambl.
AI might be leveling the skill field for everyone, including potentially giving entrepreneurs a “personalized cofounder.”
Humanoid robots can help solve the labor shortage

A September 2023 World Robotics report highlighted that robot installations in the US were up by 10% to 39,576 units in 2022, almost matching the all-time peak level of 40,373 units achieved in 2018. However, factory robots are often limited to single tasks and environments, limiting their adaptability and long-term value. The promise of robots built in the form of humans is that they can fit and travel freely inside our built environment; and with the latest advancements in AI, they will become infinitely adaptable to perform almost any manual task assigned to them.
Of note, humanoid robots, exemplified by Agility Robotics' bipedal robot Digit, are on the brink of mass production. Agility is gearing up to significantly scale its production capabilities in its upcoming Oregon-based factory. The factory is expected to churn out over 10,000 Digits annually.
This first large-scale production run signals the start of a gradual deployment of such robots to address chronic, worldwide labor shortages and an opportunity to reduce common labor dangers, like workplace injuries and burnout. By the 2030s, these robots will redefine human blue-collar roles in ways similar to how generative AI is rapidly transforming white-collar jobs today.
In a parallel development, Fourier Intelligence's GR-1 humanoid, designed to carry substantial weight, hints at a future where robots could assist in rehabilitation therapies, aiding individuals in regaining mobility. Unlike Agility, Fourier dispatches its robots to diverse R&D partners, aiming to refine the GR-1's capabilities.
At the same time, Tesla is enhancing its Optimus robot's autonomous operations, with a highlight being its self-calibration system aiding in task-learning efficiency. Optimus's deliberate, precise movements signal a step towards robots acquiring a more nuanced interaction with their environment.
In our previous newsletter, we discussed the increasing power of worker unions due to labor shortages. However, as humanoid robot production escalates and their functionalities diversify, these robots will address a significant portion of these labor gaps. Such innovations could swing the advantage to companies, which can opt to entirely automate their production processes, particularly in the manufacturing and logistics sectors. According to Precedence Research, the global humanoid robot market is expected to reach USD $28.66 billion by 2032, with a compounded annual growth rate of over 33 percent from 2023 to 2032.
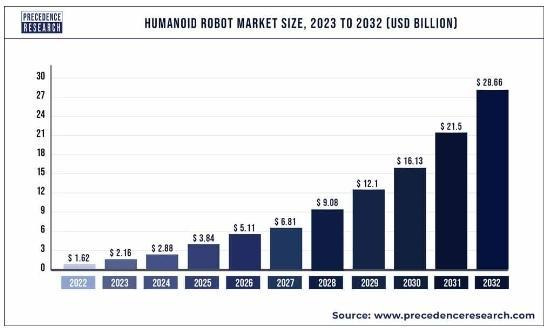
Actionable trend insights as humanoid robot production increases
For entrepreneurs: Over the coming decade, expect entrepreneurs to launch a diverse collection of Robotics Rental Services as the demand for humanoid robot assistance grows in different sectors. By renting out humanoid robots for tasks like day labor, construction, security, senior care and assisting those with physical disabilities, even serving as wait staff at events, entrepreneurs can offer a budget-friendly option for customers who need these services temporarily. On another note, offering services to change a robot's functionality, look, or the way they interact to meet personal or business preferences can fill a unique market need.
For corporate innovators: By deploying humanoid robots to handle repetitive and mundane tasks, corporations can redirect their human resources towards more strategic and creative roles, boosting productivity and enhancing employee satisfaction. Companies can also integrate collaborative robots (cobots) in manufacturing and construction processes. By taking over hazardous tasks, these cobots not only safeguard human workers but also expedite various processes, reflecting a blend of human intelligence and robotic precision.
For public sector innovators: Governments can use humanoid robots in disaster response and search and rescue operations, navigating challenging terrains and providing real-time data. Robots can also assist in space explorations and experiments, particularly in future human colonies. The public sector can also establish educational programs in schools and community centers to foster a better understanding of robotics technology, encouraging the younger generation to explore careers in this field.
Outside curiosities
This virtual reality reimagination of the game Cyberpunk 2077, using NVIDIA's RTX4090 graphics card, demonstrates the future of VR games and experiences.
Writer Vauhini Vara discusses how ChatGPT helped her writing to become viral and why that might not be a good thing.
Watch Mark Zuckerberg’s first interview in the Metaverse with hyperrealistic avatars.
Well Woven's "Unraveling Stories" rug series encodes data through patterns, visually documenting 59 endangered global textile traditions impacted by modern and environmental challenges.
A deepfake video of YouTube entrepreneur MrBeast selling 10,000 iPhone 15 Pros for USD $2 each went viral on TikTok.
Apparently, alligators can be emotional support pets, too.
More from Quantumrun
Read more daily trend reporting on Quantumrun.com
Subscribe to the Quantumrun Trends Platform (free for premium newsletter subscribers).
Corporate readers can review our Trend Intelligence Platform
Email us at contact@quantumrun.com with questions or feedback.
Finally, share your thoughts in the Substack comments below. We love hearing from you!
David Tal, Quantumrun President: Interested in collaborating with the Quantumrun Foresight team? Learn more about us here.
See you in The Futures,
Quantumrun



