The Futures - No. 42
The US vs OPEC oil showdown / Engineered diseases are the next weapons / The new police robo-K9s
In this issue
The Quantumrun team shares actionable trend insights about how the US is gaining the upper hand in oil geopolitics, militaries considering using synthetic plagues, robot dog Spot’s rising career in law enforcement, and the US’ record electric vehicle sales.
Future signals to watch
Massachusetts State Police deployed Boston Dynamics' Spot at a shooting incident in Danvers, showcasing the evolving role of robotics in handling dangerous situations. The police, equipped with two Spot robotic dogs, used these machines against barricaded suspects because they can open doors and climb staircases as part of their broader tactical response strategy.
A multinational firm in Hong Kong was defrauded of US$25.6 million through deepfake technology, where scammers used digital replicas of company executives, including the Chief Financial Officer, in video calls.
Health Canada approved Remilk, an Israeli food tech company, to sell its lab-grown milk protein in Canada, offering an animal-free alternative to dairy products.
Vertex Pharmaceuticals is set to seek US approval by mid-2024 for a groundbreaking non-opioid painkiller that effectively reduces post-surgical pain without addiction risks, potentially generating over $5 billion in annual sales.
Gravitricity is repurposing a decommissioned mine (one of Europe's deepest) in Finland into a novel underground energy storage system using gravity, merging the benefits of lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro storage.
Police departments are adopting AI technology to analyze vast amounts of unreviewed body-cam footage to identify problematic officers and behavioral patterns.
QuEra Computing aims to outpace the world's fastest supercomputers by launching a 10,000-qubit quantum computer by 2026, starting with a 10-logical-qubit machine by the end of 2024.
In 2023, the US saw a record increase in electric vehicle (EV) sales, reaching approximately 1.2 million units, which accounted for 7.6% of all vehicle sales. Despite the significant uptake of EVs, electricity generation in the country surprisingly decreased by 1.1% through November 2023, indicating that increased EV adoption did not lead to higher electricity consumption as might have been expected.
Culturally // Trending
YouTube → A Quiet Place: Day One // X → Celine Dion at the Grammy’s // Reddit → Creative carjacking // TikTok → SoftGirl // Instagram → Disney 🤝 Fortnite // Spotify → “Hiss”
💡 Watch Quantumrun’s trend videos on Linkedin & YouTube & Instagram & TikTok
🛢️ US oil production may cripple OPEC growth through the 2020s
In 2023, US oil production surged, achieving a record high of 13.5 million barrels per day and on track to exceed 14 million. This escalation, largely propelled by advancements in fracking technology, has positioned the country as a dominant force in oil production, rivaling traditional powerhouses like Saudi Arabia.
The strategic consolidations and mergers within the US energy sector, particularly in the Permian Basin, have further bolstered production efficiency, presenting a formidable challenge to the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and their capacity to sway oil prices and market shares. The increasing output from non-OPEC countries, such as Guyana, Canada, and Brazil, adds to this dynamic, diluting OPEC's influence over the global oil supply.
Historical maneuvers by Saudi Arabia to counterbalance the rise in US production included the notable market flood in 2014, which plummeted oil prices from $110 to $50 by January 2015, and the unprecedented production levels in 2020 leading to negative oil prices in the US. However, the US oil industry's capacity to swiftly adapt production in response to market signals, as seen with the price adjustments following geopolitical events like the Russian invasion of Ukraine, signifies a shift towards a more competitive and resilient energy landscape. This evolving dynamic suggests a diminishing effectiveness of OPEC's traditional levers of power to control the market, potentially curbing its growth and influence throughout the 2020s.
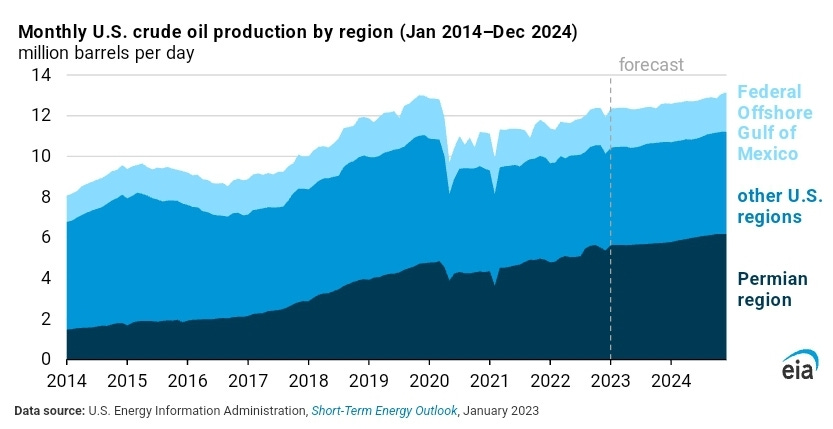
These collective trends will influence US foreign policy to adopt a more inward-looking approach during the 2020s and 2030s (barring any Black Swan event). The drive towards energy independence not only enables a reevaluation of the country’s engagements in the Middle East but also offers leverage in geopolitical negotiations, reducing the strategic need to intervene or maintain presences in oil-rich and conflict-prone regions. This transition aligns with broader global trends towards renewable energy sources and efforts to combat climate change, further influencing the US’ strategic recalibration to green energy financing and investments.
Actionable trend insights as the US oil industry slows down OPEC’s growth
For entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs in North America can examine options to reshore their supply chains by the late 2020s. If manufacturing and shipping cost reductions are realized, then future product offerings will not only be more profitable but also environmentally friendly due to shortened shipping requirements.
Entrepreneurs can pioneer hybrid energy solutions integrating renewable sources with traditional oil and gas. An innovative use case could be the development of micro-grid systems that use AI to optimize the mix of renewable energy and locally produced oil and gas for remote or underserved communities.
For corporate innovators
North American factory operators and manufacturers from all verticals now have access to the cheapest, most geopolitically secure, and most stable carbon energy production in the world. These low energy input costs will give these operators a competitive advantage for decades but will require hundreds of billions in CAPEX investments to rebuild and expand factory and manufacturing infrastructure on the continent. Central and South American nations will also benefit from feeding to resurgent North American supply chains. This represents an economic growth story to be realized by the late 2020s.
Companies can develop advanced predictive analytics platforms tailored to the oil industry, focusing on forecasting the impacts of US oil production trends on global oil prices and OPEC strategies. One specific application could be creating a real-time analytics service that uses satellite imagery, IoT sensor data from oil fields, and machine learning to provide oil producers and investors with insights into production levels, storage capacities, and transportation bottlenecks.
For public sector innovators
Agencies can implement incentive programs encouraging oil companies to adopt carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. An actionable use case involves offering tax breaks or grants to companies that integrate CCS into their extraction and refining processes, effectively reducing the carbon footprint of increased US oil production.
Governments in North America can explore policies that ease various levels of environmental and zoning bureaucracy to approve and accelerate the construction of domestic energy infrastructure and industrial facilities. Similar efforts needs to be applied to encourage cross border commercial trade and integration. Early efforts will pay dividends as the energy sector in the US continues to mature.
Trending research reports from the World Wide Web
Sustainability by Numbers thinks global energy demand could decrease by 2050 due to electrification and increased decarbonization.
A study in JAMA Pediatrics found that 12-month-olds who watched TV or DVDs were twice as likely by age 36 months to have sensory processing issues, with each additional hour of screen time after 18 months increasing the risk by about 20%.
Battery sales are surging along an S-curve typical of disruptive technologies, doubling every two to three years with a 33% average growth rate over thirty years, accelerating to 40% in the past decade due to the rise of electric vehicles.
The World Health Organization's International Agency for Research on Cancer predicts a 77% increase in global cancer cases to 35 million by 2050, driven by aging, obesity, and tobacco and alcohol use, from 20 million cases in 2022.
China's population decreased by two million in 2023, continuing a trend influenced by a declining fertility rate now nearing 1.0, significantly below the replacement level.
🦠 Engineered pathogens are the next warfare tactic
Last week, we talked about how global powers are increasingly integrating digital technology and autonomous machines into their military strategies. Now, it looks like they're adding a new, more dangerous weapon to their arsenal: lab-made diseases. A January 2024 report by the RAND Corporation (funded by the US Office of the Secretary of Defense and the National Defense Research Institute) points out a shift from using these synthetic pathogens in hypothetical scenarios to real-world applications. This change is driven by big leaps in science, like mRNA vaccines, CRISPR gene editing, and brain-computer interfaces (BCIs).
In the past, countries were cautious about using biological weapons because they were unpredictable and had a high risk of hurting their respective civilians. However, discoveries are enabling more specific and controlled use of these biological agents. There's increasing interest in making diseases that can target specific DNA. Even though there were previous attempts, like Al Qaeda trying to make anthrax weapons, today's breakthroughs are making it easier to create diseases that are harder to track and can hurt target groups more effectively (and quietly).
However, only a few countries and groups have the science facilities that could effectively contain and manipulate these diseases. The RAND report highlights the growing number of top-security labs (BSL-4 labs) that work with the most dangerous diseases, from about 10 in Europe in 2000 to over 40 by 2023. Asia is also seeing the construction of many new high-security labs in countries like the Philippines and India by 2024. While these labs are meant to help with medical research and making vaccines, their presence also increases the risk of biological weapons spreading.
Actionable trend insights as synthetic plagues are used in warfare
For public sector innovators
Public health agencies must collaborate with peers internationally to develop or strengthen a global pathogen detection network leveraging environmental DNA (eDNA) sampling technologies. By analyzing eDNA from water sources, air filters, and soil samples, agencies could identify the presence of synthetic pathogens before they result in human outbreaks.
International regulatory bodies could establish a synthetic pathogen treaty with rigorous global surveillance and reporting requirements. This framework would mandate sharing genomic data related to new pathogens, whether naturally occurring or synthetic, among signatory nations.
Outside curiosities
Is Apple turning the Vision Pro into a luxury fashion accessory?
At the heels of the Stanley tumbler frenzy, the brand launched its apparel line (and it could be the next online obsession).
Wilson is releasing its 3D-printed, airless basketballs worth $2,500.
UK-based Lincolnshire Wildlife Park has some very profane parrots (but a rehabilitation program is underway).
More from Quantumrun
Read more daily trend reporting on Quantumrun.com
Subscribe to the Quantumrun Trends Platform (free for premium newsletter subscribers).
Corporate readers can review our Trend Intelligence Platform
Email us at contact@quantumrun.com with questions or feedback.
Finally, share your thoughts in the Substack comments below. We love hearing from you!
Interested in collaborating with the Quantumrun Foresight team? Learn more about us here.
See you in The Futures,
Quantumrun





