The Futures - No. 51
Critical industries struggling to hire young workers / AI agents to automate even more tasks / The first successful pig liver transplant
In this issue
The Quantumrun team shares actionable trend insights about young workers refusing unsustainable critical industries, AI agents becoming increasingly complex, business schools integrating AI into courses, and the first successful pig liver transplant into a human.
Future signals to watch
Business schools are incorporating AI into their curriculums and coursework, including short "15-minute bursts" of AI use, to maintain graduate competitiveness and adapt to technological advancements. Additionally, some schools are developing specialized AI chatbots to teach students soft skills, such as making presentations.
Researchers have created an economical solar-powered system to transform saltwater into freshwater, potentially revolutionizing clean water access worldwide.
The US Department of Energy projects a significant boost in geothermal energy, potentially supplying 10% of the US's electricity by 2050.
Amidst consumer backlash against the "AI look," creators and agencies are employing strategies like adding imperfections and writing detailed prompts to make AI-generated images more appealing.
Footage shows Ukrainian drones using explosives to destroy Russian robotic grenade launchers, demonstrating how unmanned systems combat each other.
Startup BioOrbit uses the unique conditions of space to perfect the crystallization of proteins for drugs, a potential breakthrough for immunotherapy (a promising cancer treatment).
Microsoft and Quantinuum achieved a groundbreaking quantum computing milestone by demonstrating the most reliable logical qubits to date, leveraging a qubit-virtualization system for error-free quantum experiments.
American Richard Slayman receives the world's first successful transplant of a genetically modified pig kidney, offering new hope for those with end-stage renal disease. This pioneering procedure used a kidney with removed pig genes and added human ones to ensure compatibility, signifying a promising advancement in xenotransplantation (inter-species organ transplant).
Forward this email to a friend and help The Futures reach a wider audience :)
Culturally // Trending
YouTube → Joker: Folie à Deux // X → Eclipse 2024 // Reddit → Watching history // TikTok → Everything I ate today // Instagram → Abu Dhabi’s eSports Island // Spotify → “II Most Wanted”
👷 Young workers are not attracted to many critical industries
In a global economy increasingly reliant on sustainable practices and technology, the mining industry is encountering a workforce paradox. Despite the surging demand for critical minerals essential for clean energy technologies—such as lithium for electric vehicle (EV) batteries, whose demand surged by 300% from 2017 to 2022—the sector struggles to attract young professionals. This reluctance stems from the industry's reputation for environmental degradation and labor exploitation, overshadowing its crucial role in the green transition.
The transition to clean energy requires vast amounts of minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, a practice viewed skeptically by the next generation of ethical-minded workers. Efforts by programs like Mineral-X at Stanford University aim to reinvent mining with a focus on sustainability and community engagement. However, the broader challenge remains: reversing the declining enrollment in mining-related university programs and the overall industry image to meet the escalating demand for critical minerals.
Beyond mining, labor shortages are impacting supply chains across various sectors due to factors like climate change, public health concerns, and shifting demographic trends. Developed countries face aging populations and restrictive immigration policies, contributing to a dwindling workforce. These shortages are not limited to high-skill jobs but also affect essential blue-collar roles, critical to maintaining the supply chains necessary for everyday operations. The growing pressures from climate change is worsening the situation, with rising temperatures reducing worker productivity and contributing to supply chain disruptions.
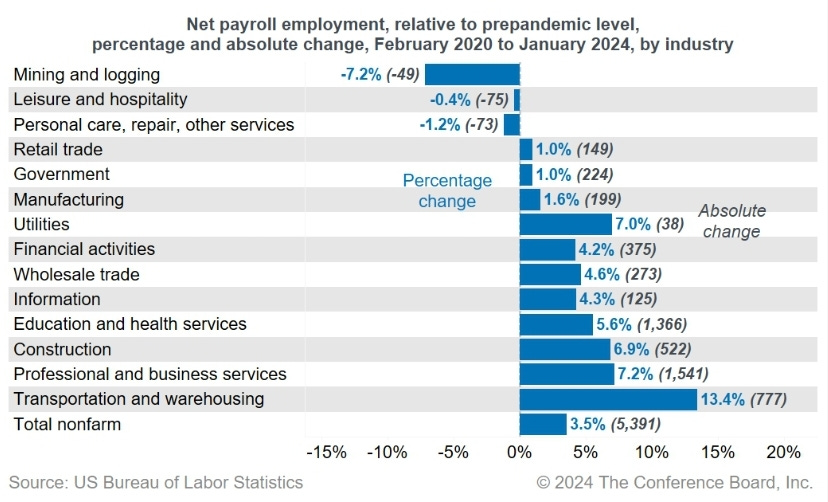
Labor shortages also significantly affect high-stakes industries such as healthcare, law enforcement, and aviation, where understaffing poses direct risks to public health and safety. The "Great Reshuffle," a term coined to describe the mass movement of workers seeking better work-life balance and compensation post-COVID-19 pandemic, has led to critical gaps in these sectors. The situation is compounded by an aging population and a tight labor market in the US, making it difficult to meet the demand for skilled workers.
As such, several companies are developing humanoid robots that can be trained by humans to supplement the blue-collar workforce. For example, Carnegie Mellon University researchers created H2O, a framework that enables real-time teleoperation of a full-sized humanoid robot by a human using just an RGB camera.
Actionable trend insights as critical industries struggle to find workers:
For corporate innovators
Companies can invest more seriously in employer branding activities to market their companies, their industries, and the professions they hire to ever younger students, e.g., high school, or even middle school. These activities could include subsidized school field trips to factories, subsidized shop classes, blue-collar career days, etc.
Companies can adopt next-generation robotics and automation technologies to perform tasks that are traditionally labor-intensive and have high vacancy rates due to labor shortages. For instance:
Mining companies can utilize autonomous mining vehicles and diggers to mine in remote locations 24/7.
Construction companies could deploy a fleet of drones equipped with advanced imaging technologies to map out a construction site, assess the work progress, and identify potential hazards, reducing the need for manual labor in dangerous or hard-to-reach areas.
Hospital networks can Invest in a network of mobile health clinics staffed with AI-powered diagnostic tools and telehealth capabilities to serve rural and underserved communities. For instance, these clinics could be equipped with AI that interprets medical images or conducts preliminary health screenings, supported by telehealth sessions with healthcare professionals, bringing critical healthcare services to areas that traditionally suffer from a lack of medical staff.
For public sector innovators
Governments can explore increasing subsidies to post-secondary institutions—potentially even offering free college tuition—to students studying for professions in targeted, high-value, low-recruitment industries.
Governments can implement a national digital credentialing system that recognizes and standardizes non-traditional learning and skill acquisition, such as online courses, workshops, and real-world experience, across critical industries facing labor shortages.
For example, a healthcare professional with years of hands-on experience (including from foreign countries) and specialized online certifications could be quickly credentialed for urgent roles in underserved areas, streamlining the hiring process and addressing critical labor shortages more effectively.
Government agencies can launch a pilot project to integrate autonomous vehicles into public transportation fleets, specifically targeting routes and times that are underserved due to driver shortages. An example use case could involve using these autonomous buses to provide reliable, 24/7 public transportation options in suburban and rural areas, improving mobility for residents and reducing the reliance on personal vehicles.
Trending research reports from the World Wide Web
Deloitte discusses how AI is fast-charging government services, from automating tax filing to establishing smart cities.
The Reach discusses Google's existential challenges amidst the rise of AI, emphasizing its struggle to adapt its business model and maintain relevance amid AI advancements and changing user expectations.
According to iCIMS’ March 2024 Workforce Report, despite fewer women applying, they still get hired for half of the six-figure job posts.
Based on the 2024 Edelman Trust Barometer survey, respondents trust the tech industry (76%) but not AI (only 50%).
📱AI agents are evolving beyond chatbots
The increasing developments in AI agents can reshape the way we work and interact with digital tools, making everyday tasks simpler and more efficient. These agents are programmed to autonomously complete tasks by processing human language, accessing vast information databases, and executing actions without direct human intervention. For example, NVIDIA is collaborating with healthcare startup Hippocratic AI to create AI healthcare agents (Polaris) capable of performing tasks traditionally done by nurses. Polaris performed better than humans in identifying lab result ranges (96% versus 94% for human nurses) during benchmark testing.
An example of Hippocratic AI’s nurse agent
Another area seeing rapid innovation is personalized AI assistants. For example, the 01 Light device by startup Open Interpreter transforms how users interact with their computers, enabling voice-controlled management of various tasks. It supports a range of functions, from sending emails and editing documents to browsing online, all without the need for physical interaction. Furthermore, its open-source nature and compatibility with Wi-Fi or hotspot connectivity make it a versatile tool for remote computer access, offering a glimpse into the future of personal AI assistants.
The impact of AI agents extends across multiple sectors. They offer the potential for increased efficiency and data-driven decision-making in businesses, leading to cost savings and improved customer service.
Meanwhile, MIT’s research into socially embodied AI agents is exploring how these technologies can enhance human-to-human interactions, focusing on multi-person scenarios beyond traditional one-on-one human-robot interactions. Projects like the DYADIC-MODEL and MHRI-DESIGN are investigating family dynamics and shared activities, aiming to use AI to strengthen relationships and improve social interactions.
However, the rise of AI agents also raises important considerations, including the potential displacement of jobs, ethical concerns around data privacy and security, and the need for comprehensive regulation to manage these advanced tools.
Actionable trend insights as companies invest in AI agents
For entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs can develop AI agents as collaborative partners to innovate within creative industries, such as fashion, art, and entertainment. Human artists and creators can use these agents to bounce ideas with and generate out-of-the-box concepts using AI’s vast database.
Digital gaming businesses can use AI agents to create dynamic, narrative-driven experiences that evolve based on player choices and interactions. An application could involve an AI-driven platform where stories unfold differently for every user, influenced by their decisions, creating deeply personalized and immersive storytelling experiences.
For corporate innovators
Companies that operate highly routine and automatable industries may need to reassess their digital infrastructure to ensure they can safely operate next-gen AI platforms in a manner that protects their data and internal IP.
Companies can develop personalized AI agents tailored to enhance employee productivity and job satisfaction. For instance, a company could introduce AI agents for each employee, and as collaborators, these employees can train their AI agents to automate many of their routine tasks.
For public sector innovators
Governments can integrate AI agents with emergency dispatch systems to enhance response strategies for natural disasters or urban crises. For example, during a flood, existing forecasting systems could predict water levels and flow paths, and then AI agents can help direct first responders to the most vulnerable locations while also managing logistics for shelters and medical care.
Government agencies can use AI agents to provide basic information and government services, such as directing queries to the right department, updating citizens’ information, and processing simple document requests. For example, agencies can install AI agent kiosks in public places to enhance access to government services and reduce work for human administrators.
Outside curiosities
The April 2024 eclipse tourism resulted in fully booked AirBnBs and hotels along the eclipse’s path.
Beauty brands are releasing anti-marketing campaigns for tweens obsessed with skincare.
Celebrities are releasing their alcohol brands even amid a growing number of young people who are embracing the Sober Movement.
Millennials are all about that soft life.
Augmented reality (AR) is making weather reporting cool.
More from Quantumrun
Read more daily trend reporting on Quantumrun.com
Subscribe to the Quantumrun Trends Platform (free for premium newsletter subscribers).
Corporate readers can review our Trend Intelligence Platform
Email us at contact@quantumrun.com with questions or feedback.
Finally, share your thoughts in the Substack comments below. We love hearing from you!
Interested in collaborating with the Quantumrun Foresight team? Learn more about us here.
See you in The Futures,
Quantumrun